Pittsburgh Vein and Vascular Lab
PHYSICIAN TRAINING AND CERTIFICATION
When choosing a Vein Clinic or Vascular Lab to entrust the care of your legs, there are several things to consider. Foremost is the skill and training of your physician. Our Physicians are Board Certified in Surgery and have years of experience treating veins with great outcomes in both comfort and appearance. Their treatment philosophy encourages them to offer a full range of treatment modalities to treat the entire spectrum of vein disease. All treatments begin with a very thorough Vein exam that includes a Doppler Ultrasound exam.

LAB TECHNOLOGIST CERTIFICATION
All of the Ultrasound techs at the Advanced Vein Center are Registered Vascular Technologists (RVTs)! This is a certification that reflects extensive training past simply attending ultrasound school. The ARDMS (American Registry of Diagnostic Medical Sonographers) is the national certifying agency. It has very defined requirements. Ultrasonographers must pass two very difficult certifying exams. The areas tested on the exam are a physics portion and a portion that reflects their specialty. Our RVTs are specifically certified in lower extremity venous mapping and exams.
LAB ACCREDITATION
Our lab has achieved Ultrasound accreditation from the ACR (American College of Radiology). The Advanced Vein Center prides itself on maintaining this very strict and regulated accreditation based on quality control criteria. If your vein center is accredited by the ACR, it shows a dedication to the quality care and treatment of patients, following only the highest standards.
When to Visit Our Vein Lab and Clinic
When you have Spider Veins…
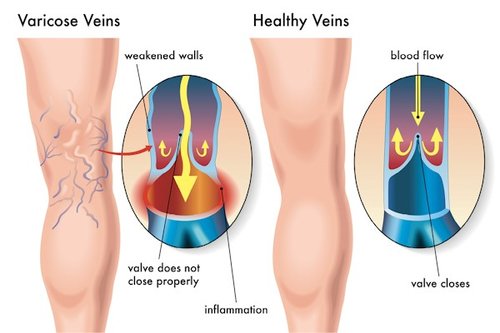
Dilated blood vessels, called spider veins, are small purple or red veins that can form from a trauma when hit. They are smaller in size by comparison to a varicose vein, but are often more noticeable and darker because they are toward the skin’s surface. Women are more at risk for acquiring spider veins as they can be triggered through hormonal variations, such as hormone replacement therapy or pregnancy. Symptoms of spider veins include Charley horses, restless leg syndrome, night cramps in the arch or calf, itching, minor pains and aches. Spider veins can be found on the chest, face (sides and on nose), legs and ankles. Commonly considered to be an aesthetic problem, spider veins may be an indication of serious vein disease beginning below the skin’s surface. The only way to tell for sure is a Venous Doppler Ultrasound exam.
When you have swollen legs, calf cramps, tired achy legs,…
These are symptoms of vein disease. It’s also something we can help alleviate. You don’t have to live in pain. Our Registered Vascular Technologists (RVTs) will spend about an hour per leg mapping your veins to provide our physicians with an accurate road map to create your own personal treatment plan to treat your painful leg symptoms.
When you have thick ropey painful varicose veins…
Most patients varicose vein procedures are covered by insurance. The Doppler Ultrasound Exam is a required first step to verify Medical Necessity, and to make sure your symptoms are caused by venous reflux, which we can treat at the Advanced Vein Center.
When you have a sudden onset of pain and swelling in only one calf or ankle …
You may have a DVT (deep vein thrombosis) which is a life threatening problem that needs to be addressed immediately. If this describes you, call immediately.
What Causes Spider Veins?
Spider veins is a common vein problem which is also known as telangiectasias. These veins are often small, are blue or purple and are less dangerous form of their counter part varicose veins. Also, their appearance is like spider webs which is the reason they are called spider veins. Unfortunately, the main causes of spider veins are hard to find, yet there are some reasons that are a lot likely to cause you spider veins, here are few of them:
- Genetics
Genetics play an important role when it comes to spreading diseases, and spider veins isn’t an exception. Just like many other health problems, spider veins can to transferred from one generation to another. Maybe your parents or grand parents have suffered from this problem in past and if that’s the case then this may be the reason you are deal with this problem too!
- Age
As you age, your blood vessels lose elasticity and become more prone to damage, increasing the likelihood of developing spider veins.
- Gender
Women are more likely to develop spider veins than men, possibly due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, menopause, or the use of birth control pills.
- Pregnancy
The increased pressure on the veins during pregnancy can lead to the development of spider veins. Standing or sitting for long periods: Sitting or standing for long periods can increase pressure on the veins in the legs, leading to the development of spider veins.
- Obesity
Excess weight can increase pressure on the veins and lead to the development of spider veins.
- Sun exposure
Prolonged exposure to the sun can cause damage to the skin and blood vessels, leading to the development of spider veins.
In summary, spider veins are caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors, including age, gender, pregnancy, prolonged sitting or standing, obesity, and sun exposure.
What to Expect when having a Doppler exam
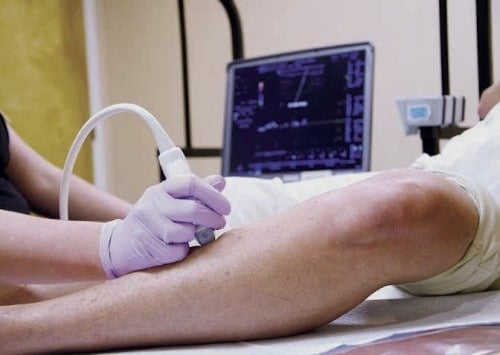
After a thorough History and Physical, you will have a Doppler Ultrasound Exam. The RVT will use a Transducer to gently and completely scan your leg veins. This is very similar to an Ob ultrasound exam when the technician views the baby with the ultrasound probe. It is non-invasive and does not cause discomfort.
The transducer is so sensitive that our Vein Doctor can watch the vein valves opening and snapping shut. We then measure how many seconds it takes the vein valve to snap shut, and if blood leaks backwards down the leg vein and causes swelling it is called reflux. Treatment for reflux is covered by most insurers. Depending on the size of the abnormal veins and the severity of the reflux, our physician will discuss the recommended treatment options to prevent many of the complications that come from untreated progressive vein disease.
What is a Venogram? What is Phlebography?
Lower leg venography is used to study the veins in the legs. Phlebography is an x-ray test used to study the veins of the body.
Why your Doctor may order a venogram or phlebography
These tests may help:
- Assess the functioning of deep leg vein valves
- Diagnose deep vein thrombosis (DVT)—a blood clot deep within the leg that may lead to a pulmonary embolism, which is an obstruction of a blood vessel in the lungs
- Find a good vein for a graft for bypasses
- Find blockages or vein obstructions
- Assess congenital vein problems and birth defects
Complications
Problems from the procedure are rare, but all procedures have some risk.
Your doctor will review potential complications, for example:
- Blood clots
- Infection
- Phlebitis -Inflammation of a vein
- Damaged tissue
- Contrast material allergic reactions
- Damage to kidneys
Prior to the test:
Drink only clear fluids or fast for four hours before the test. If you are nervous about the test, your doctor may give you a sedative. Arrange for someone to drive you home.
Description of test
The test takes approximately 30 minutes.
You will lie on a tilting x-ray table. The area where the catheter will be inserted will be cleaned. A small cut in your skin may be made in that area. You may be given a local anesthetic to numb the area where the catheter will be inserted.
After a catheter is gently placed into your vein, the contrast will be slowly injected. A tight band may be tied around your ankle or your lower body may be tilted. This helps to fill the veins with contrast. You will be asked to remain still as the doctor uses an x-ray machine to view the movement of the contrast through your veins.
Will the test be painful?
It may be sore at the injection site during the test and tender for a few days after. Some people feel mild discomfort throughout the body, or nausea as the contrast fills the veins.
After the test
Usually no more than a band aid is needed to be applied the site of the injection after the catheter is removed.
In general:
- Take it easy for the rest of the day and avoid any strenuous activity.
- Drink a lot of fluid for 24 hours to flush the remaining contrast from your body.
- You may shower and remove the bandage the day after your test.
- Observe the injection site for any swelling, heat, redness, pain, or drainage. The injection area may be sore for a few days.
- Put pressure on the site for at least 10 minutes if any bleeding or swelling occurs at the injection or puncture site.
Ask your doctor about when it is safe to shower, bathe, or soak in water. Most people are able to return to normal activities the day after the test.
Notify Your Physician if:
- Signs of infection , including fever or chills
- Swelling, redness, or pain at the injection site
- Itching, rash, or other signs of an allergic reaction
Results
A normal venogram reveals that the blood flow through the vein is normal. An abnormal venography means that there is something blocking blood flow through the vein. If the results are not normal, your doctor will explain possible further studies or treatment
What are the benefits of early detection of vascular diseases?
There are so many benefits of detecting vascular diseases much earlier, and here are some of those:
- Early Treatment:
Early treatment means you can easily catch the disease in its early stages, which is much easier to deal with than it’s later stages. Also, it parents the problem from getting worse and helps you avoid it from reaching the other parts of the body. Not to mention, an underdeveloped disease is much weaker, so it will heal rapidly once early treatment is done.
- Prevention of Complications:
Did you know vein problems can lead to terrible conditions if not treated well or left untreated for a long time? The first bad thing is pain, which is mostly common with Varicose veins. However, sometimes ignorance can lead to blood clots, bursting of the affected vein, irregular blood circulation and even amputation if the problem is too serious.
- Improved Quality Of Life:
If you can treatment something early, then why wait? Living with a medical condition isn’t fun at all, as it makes like just difficult, no one wants to deal with constant pain, disturbance and continuous medications until the problem doesn’t go away. You might even need to visit doctor multiple times for a worse condition, which will cost a lot of time and money.
What lifestyle changes are recommended if a vascular condition is detected?
If a vascular condition is detected, try following these tips as soon. As possible to prevent it from getting worse.
- Avoid Alcohol and Smoking: Alcohol and Smoking for everyone, but even worse for those suffering for vascular condition, as it slow downs healing process and makes it difficult to circulate blood throughout the body.
- Weight management: Consider losing some weight to avoid putting pressure on your circulatory system.
The Advanced Vein Centers that have DVT Checks and Ultrasound Vein Tests are Bridgewater, Bridgeville and Cranberry.
Vein Testing FAQ’s
Ultrasound does not have any harmful side effects and doesn’t use ionizing radiation.
With 39 years of experience, Dr. Thomas Kavic, MD specializes in Diagnostic Radiology and Radiology. Dr. Kavic is affiliated with Heritage Valley Beaver, Heritage Valley Sewickley and East Liverpool City Hospital.
Publications include:
- Kavic,T.A., Kimbrow,L. “Sonographic Evaluation of Frozen Venous Valves.”
His memberships include:
- American College of Radiology – ACR Fellow
- Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound Member
Usually one Diagnostic Ultrasound per leg is all you need to begin a treatment plan. Depending on your insurance company’s guidelines, it is recommended to have a vein ultrasound after each treatment and every six months to monitor your progress, as vein disease is chronic and progressive.
Wear comfortable, easy to change clothes. You will be given elastic shorts to wear if you like. For a lower extremity vascular exam you do not need to fast, however the caffeine in coffee may affect some patients. Better results are obtained later in the day.
The Doppler Exam is painless and we make every effort to keep you comfortable. The RVT will apply a warm non-staining gel onto your leg allowing the transducer to easily slide along your leg, giving a smooth unobstructed view of your veins. At certain key points, digital pictures of your veins are taken and later measurements are taken. Sometimes the transducer is pressed firmly into areas like behind the knee, but this is usually well tolerated. Afterward the gel is wiped off and you can immediately resume normal activity.
Ultrasound uses sound waves to produce pictures of your veins and other soft tissues in the body. Sonography, performed by our Registered Vascular Technicians, uses a probe called a transducer to emit sound waves of a very high frequency undetectable to the human ear, like radar, to bounce off the structures in your leg. These waves are transformed by the computer into a digital image. It can show blood flowing through the veins and allows the timing of the flow of the blood to qualify your symptoms. This allows our vein doctor to evaluate your veins in a very safe and comfortable manner with a high degree of accuracy.
DVT stands for Deep Vein Thrombosis and can be life threatening. It can break loose and move to your lung causing a localized blockage. You may have trouble breathing. Blood clots in the lung are called a pulmonary embolism.
A DVT is a medical emergency. Seek medical care immediately.
The only way to be sure is to have a Doppler Ultrasound exam at an a ACR accredited vascular Lab like the Advanced Vein Center.
Call our office at 724-987-3220 to schedule an appointment. If our office is closed seek immediate assessment at an ER or urgent care facility.
When a blot clot from the deep veins of the calf break off and travels to the lung, blocking flow, it is called a pulmonary embolism. It is a medical emergency and is life threatening, killing almost 200,000 people a year.
The most important step is early recognition and identification of a deep vein thrombus (blood clot). If you have no history of having a DVT, or receiving prior treatment of a DVT you should be admitted to the hospital for care. IV blood thinners are generally initiated.
Treatment goals for DVT are to immediately start thinning the blood with an IV medication like Heparin to keep the clot from growing any bigger. If the clots are large, or multiple, your Doctor may recommend a filter to catch clot pieces that break off to prevent them from getting into the lungs. A plan will be developed to prevent new clots from forming; this is often accomplished from a prescription of Warfarin (Coumadin) for nine months and for some at risk individuals, may last a lifetime. The painful symptoms, swelling and discoloration, will also be addressed to prevent the vessels from sustaining permanent damage.
Post Phlebitis Syndrome is characterized by a lifetime of pain and swelling and occurs when the condition is not aggressively treated initially after a clot (thrombus) and permanent damage occurs to the lining of the veins in the legs.
Leg veins are the most common area to be associated with DVTs.
The most common symptom of DVTs in the leg is painful swelling of one calf more than the other, especially when you stretch your calf by bending at your ankle bringing your toes towards your nose.
In addition, if the calf is warm and the pain increases when you squeeze your calf, it is imperative to have it checked with a Doppler Exam at an accredited lab like the Advanced Vein Center.
If at any point you feel short of breath, call 911 or go directly to the emergency room, because a blood clot could travel to your lung and be life threatening.
Some people are genetically prone to get a DVT, for instance people with Protein C and S deficiency and Factor 5 deficiency. Others have medical conditions that promote DVT’s like Lupus. These medical conditions lead to “hypercoagulability” which causes them to be prone to forming a thrombus (blood clots). Examples are birth control, hormone replacement and smoking.
Injury to the area is the second component of DVT formation; being hit with a soft ball is one example.
By far the most common risk factor is surgery, especially knee and hip replacements or ankle surgery. This is why many surgeons “prophylaxis” prior to surgery, which means give the patient a medication to reduce the risk of blood clots around the time of surgery. Inflammation for swollen legs can also damage veins which may lead to the formation of blood clots.
Inactivity is a significant risk factor of forming vein thrombi. That is why on long car trips or plane rides you should get up and walk around, and after surgery, or having a baby, your doctor will insist you get up and move your calf muscles.
One of the most obvious and complicated problems caused by untreated vein disease is a draining venous leg ulcer (wound).
Sometimes it takes getting an infected leg ulcer before a patient finally makes an appointment. At the Beaver Valley Foot Clinic, Dr Teimouri specializes in the care of vein ulcers and coordinates care with the advanced Vein Center physicians creating a comprehensive program to get you on your feet again!
When going on a long trip or airline flight, it is important to wear compression garments if you have venous disease. This will prevent post phlebitic syndrome, reduce edema, and keep you comfortable.
After you have been diagnosed and treated for a DVT, these stockings must be worn daily for three years to help reduce the chance of reoccurrence.
Exercise and getting up and walking every few hours will also help prevent a vein thrombus from forming, as will keeping well hydrated.
- A phlebologist is a medical doctor which specializes in the venous system
- A vascular specialist specializes in both veins, arteries, and to some extent the heart.
- A vascular surgeon is ultimately the surgeon who will provide any type of invasive treatment to the veins.
- An interventional radiologist is an imaging specialist who takes and interprets imaging tests like venograms and ultrasound exams.
- A dermatologist is a medical doctor who specializes in conditions of the skin and nails.
