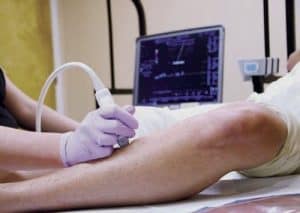
Blood Clot In Leg Overview
 What’s are Clots?
What’s are Clots?
Clots are clumps of proteins and other cells in your blood that are bound together. A clot’s purpose is to help slow the bleeding when you become injured. Clots typically dissolve as the wound heals. If for some reason it does not or if one forms when there is no injury, it can either partially or completely block a blood vessel. That’s a Blood Clot In Leg.
Medical Conditions Caused by Clots
When clots form unexpectedly, they can lead to serious health condition and even death. If a clots reaches an artery, it can cause a stroke or a heart attack. In a vein, you will notice pain and swelling. Clots that form deep inside your body are called a deep vein thrombosis (DVT). If a DVT clot moves to your lungs is called a pulmonary embolism (PE). All of these should be treated as medical emergencies.
What puts me at risk?
A blood clot can form if you break a bone or badly pull a muscle. Injuries to a blood vessel will trigger a chemical messenger that calls for the formation of a clot to help heal the injured area. You might not always know when you get a clot. Sometimes they can form without your knowledge. They can be caused by trauma like slipping on ice and falling or being in a car accident. Other injuries are less obvious; like a strain, twisted ankle, or even a bruise. Because of this you may not know why a blood clot has formed or you might not even know that you have one. However, there are clues. You are at a higher risk of developing a clot if you:
- recently had surgery,
- are immobilized or on bed rest,
- are pregnant,
- take an international flight (due to the extended period of sitting),
- are in a wheelchair,
- are obese or overweight,
- suffer from high cholesterol or diabetes or
- are 60 or older.
Blood Clot In Leg Symptoms
Signs of a Blood Clot
If you have any of the risk factors for a blood clot, then you should be on the lookout for signs that you may have one.
Change in skin color:
When a clot creates a stoppage in your legs or arms, your skin may turn slightly blue or red. Your skin may stay this color if there is permeate damage to the blood vessels. A Pulmonary embolism in your lung can cause your skin to become pale, bluish, and clammy.
Difficulty Breathing:
If you have a clot in your lung or in your heart, you may experience breathing difficulties. Your heart beat may race, your skin may become clammy, sweaty or you may faint. All of these are VERY SERIOUS medical conditions.
You should seek medical help immediately.
Dull Pain:
A clot will often cause pain where it is located. For example, in your stomach, lower leg or under your throat
Sudden Intense Pain:
Sudden intense pain, especially in the chest, may mean that the clot has broken loose and caused a Pulmonary embolism in your lung. Alternatively, it could be a sign that a clot in your artery has given you a heart attack. In the case of a heart attack, you might also feel pain in your left arm.
Swelling:
When a blood clot forms, it can slow or stop the flow of blood in your veins or arteries (similar to a dam in a river or stream.) This will cause a buildup of blood upstream from the clot. The bigger the clot, the more blood will pool above it, causing increased pressure in the blood vessel causing it to swell. If swelling occurs in the calf or lower leg, it can be a sign of DVT. Blood clots can form in almost any part of your body, not just in your legs. Clots form in the arms and the abdomen. Clots can cause permanent damage to the blood vessels. Because of this, you may still suffer from swelling, pain and sores even after the clot goes away.
Blood Clot In Leg- What to Do
Blood Clot In Leg – Prevention
Blood Clot In Leg- DVT and Pulmonary Embolism
Symptoms of clotting
Clotting can happen anywhere in the body. When a clot forms it inhibits the flow of blood This can cut off the oxygen supply and damage the surrounding tissue. Depending on where the clot is located you may notice different symptoms. If the flow of oxygen is cut to organs such as the lung or heart, it will cause life-threatening conditions that should not be ignored.
Clotting in the Lung:
If a clot forms, or more commonly, moves into the lung it can produce a pulmonary embolism or PE. A PE will bring on:
- a quickened pulse,
- chest pain,
- bloody cough and
- shortness of breath.
Call 9-1-1 right away if you or someone you love experiences any of the above warning signs.
Clotting in the Heart:
A heart attack is caused by clotting in the heart and is one of the leading causes of death in people over 40 years of age. When blood it stopped from properly flowing in the heart, the heart muscle will start to die. It is imperative that you get to a hospital right away. A heart attack may feel similar to a pulmonary embolism caused by a clot in the lung. However during a heart attack, you will often get nauseous and lightheaded in addition to feeling chest pain. Additionally, pain or numbness may radiate into the left arm and shoulder. Regardless, it is essential that you get to a hospital or call 9-1-1 right away.
Clotting in the Brain:
Clotting does not typically start in the brain unless there was an incidence of head trauma. In most cases the clot forms elsewhere and then is transported via the bloodstream to the brain. When a clot impedes normal blood flow, pressure will build up behind the clot. If a severe blockage is located in the brain, it may lead to a stroke. Your brain cells will start to die in minutes without oxygen from the blood. After just a few moments your oxygen starved brain cells will start to die and impair your mental capacities. You may notice a quick onset of a headache, seizures, confusion, weakness and speech problems. These symptoms may only occur on one side of the body.
Clotting in the Stomach:
When clotting occurs in the abdomen, symptoms can be harder to detect. Often no warning signs are presented at all. If a vein becomes blocked in the esophagus or stomach, the vein can rupture under the pressure, allowing blood to escape into the stomach. A rupture can be exceptionally painful. You may notice blood in your stool, it may look black in color and smell particularly bad. You may also start to vomit blood.
Clotting in the Kidneys:
Clots in the kidneys usually develop slowly and are most common in adults. This condition, also called renal vein thrombosis, does not normally demonstrate symptoms unless the clot breaks off and moves into your lung. In very rare cases, the clots have been known to develop quickly, causing nausea, fever, and vomiting. This type of quick-onset renal vein thrombosis is more common in children. You may notice blood in your urine. You might also have to urinate less frequently.
Are there any natural remedies or supplements that can help prevent blood clots?
While natural remedies and supplements may have potential benefits in preventing blood clots, it’s essential to approach them with caution and consult a healthcare provider before incorporating them into your routine, especially if you have an underlying medical condition or are taking other medications. Here are some options:
- Dietary Changes:
Adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall cardiovascular health, potentially reducing the risk of blood clots.
- Fish Oil:
Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil may have anticoagulant properties and support cardiovascular health. However, their effects on blood clot prevention can vary.
- Turmeric:
Curcumin, a compound in turmeric, has anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce clot formation. It’s often consumed as a supplement or spice.
- Ginger:
Ginger has potential antiplatelet effects, which might help prevent excessive blood clotting. It can be consumed in food or as a supplement.
- Garlic:
Garlic may have mild anticoagulant properties and promote circulation. It’s often used in cooking or as a supplement.
- Ginkgo Biloba:
Some studies suggest that ginkgo biloba may reduce blood clot formation by improving blood flow. However, it can interact with medications, so consult a doctor.
Can blood clots occur in arteries as well?
Yes, blood clots can occur in arteries, and this condition is known as arterial thrombosis. Arterial blood clots are different from venous blood clots. Arterial clots typically form due to atherosclerosis, a condition where cholesterol plaques build up in arteries, leading to narrowing and reduced blood flow. These clots can partially or completely block blood flow to vital organs or tissues, causing serious conditions like heart attacks or strokes. Symptoms can include chest pain, numbness, weakness, or difficulty speaking, depending on the affected artery. Prompt medical attention is crucial to dissolve or remove arterial clots and prevent severe consequences.
Can Blood Clots Case Long-Term Issues?
Yes, if left untreated then blood clots can easily lead to serious long-term health issues. It’s because when a clot has developed in a deep vein, it will arise chronic problems like post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS), which can cause pain, skin changes, swelling in the affected area. Furthermore, blood clots can develop in lungs as well, they are known as pulmonary embolisms and can even damage the lung, which can lead to long-tern breathing difficulties. This may even increase the chances of clots in future, which can make blood clots an ongoing problems, leading to even more and more problems.
How Long Blood Clots Take To Dissolve Naturally?
The time it will take a blood clot to dissolve naturally can easily vary depending on the clot’s size, location and even individual health factors. If clots are small, then they may dissolve within few weeks as body will gradually break them down. But for larger clots, especially if the ones present in larger veins can take months to fully dissolve or may even require medical treatment to speed up the process to prevent complications. You will likely need help medications like blood thinners, to help prevent blood clots from worsening.
What To Do If You Suspect Blood Clots?
If you suspect you might have blood clots, it’s important to seek medical attention right away, here’s what you should be doing:
1. Go To Emergency Room: Blood clots in legs or lungs are life-threatening especially if left untreated, so make sure to get medical attention as soon as possible.
2. Don’t Ignore Symptoms: You can experience variety of symptoms such as swelling, redness, warmth, or pain in your leg. There can be other symptoms such as sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, or rapid pulse. If you experience these, seek medical help as they are signs of blood clots.

 What’s are Clots?
What’s are Clots?