What do all those Vein words mean?
GLOSSARY OF VEIN TERMS:
Ablation: A general term describing the surgical destruction of a diseased vein. We use in the context of minimally invasive treatments for common vein conditions.
ACR: American College of Radiology
Air Plethysmography: A test designed to measure the severity of vein disease. It involves using inflatable cuffs to measure how well a vein refills after being compressed.
Ambulatory Phlebectomy: An office based procedure to remove medium sized varicose veins, allowing immediate walking post procedure.
Ambulatory Venous Pressure: The pressure inside a leg vein while a person is standing. Due to the pull of gravity, this pressure will always be higher than when the patient is laying flat.
American College of Phlebology (ACP): A leading resource for physicians and allied health professionals in the field of phlebology. Provides member resources for clinical management, patient management and patient education. In 2018 this association changed their name to American Vein and Lymphatic Society (AVLS).
Aneurysm (Vein): A focal dilation of a vein. This can be thought of as a vein “ballooning out,” usually due to elevated pressure or weakened vein walls.
Angiogenesis: The growth of new blood vessels. In the context of vein treatment, this refers to the the formation of smaller veins in the area of a larger damaged or diseased vein.
Angiomata: A benign (non-cancerous) tumor sometimes arising from the inside walls of a vein.
Anterior Accessory Greater Saphenous Vein (AAGSV): Refers to a commonly found branch of the main vein on the front of the leg, the Greater Saphenous Vein (GSV). This is also found on the front of the leg, and only occurs in about 15% of patients.
Anticoagulation: Refers to the action of blood-thinning and “clot-busting” drugs. When taken, this class of medications makes blood less likely to form clots.
ARDMS: The American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography® (ARDMS®) administers examinations and awards credentials in areas of ultrasound.
Axial reflux: Describes venous reflux (reversed flow) which occurs along large portions of the two main veins of the leg, the Greater Saphenous Vein (GSV) and the Small Saphenous Vein (SSV). This essentially means that a patient’s veins are diseased along the full length of the leg.
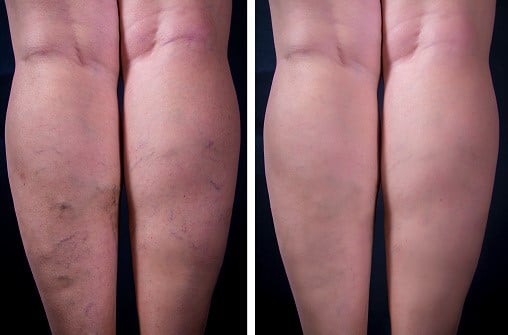
Bleeding: Varicose veins are weak walled and easily ruptured, which can lead to catastrophic blood loss.
Blood Clot: A clump of coagulated blood which forms inside a vein, particularly the veins of the leg. This is the informal name for a thrombus.
Broken valves: Incompetent valves in lower extremity veins, failure of which leads to varicosities.
Calf cramps: A leg cramp is an episode of sudden pain in the muscles of the leg caused by an involuntary contracting (shortening) of the leg muscle.
CEAP Class: A scale used to rate the severity of vein disease on a 7 point scale. CEAP stands for “Clinical, Etiology, Anatomy, Pathophysiology.”
Cerebral Venous Thrombus (CVT): A potentially life-threatening blood clot which can form inside the veins of the brain.
Charlie horses: Another name for a muscle spasm. Charley horses can occur in any muscle, but they’re most common in the legs.
Chronic Venous Hypertension (CVH): Higher than normal blood pressure within the body’s system of veins. Along with chronic venous insufficiency, chronic venous hypertension causes physical symptoms in the legs such as achiness, tenderness, swelling, and ulcers.
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI): This refers to long standing vein disease, usually in the legs. In cases of CVI, the valves which keep blood flowing in one direction (towards the heart) become leaky, causing blood to pool in the legs.
Closure procedure – VNUS®: RF (radiofrequency) Ablation system is a minimally invasive varicose vein treatment procedure that uses radiofrequency energy (electricity) to heat, collapse and seal off the targeted blood vessels.
Competent Vein: A normal, healthy, functioning vein. This is the opposite of an incompetent vein.
Compression: The reduction in volume (causing an increase in pressure) of the blood in leg veins.
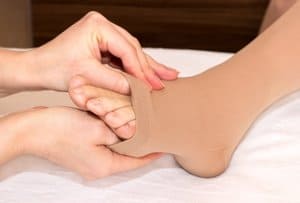
Compression (Treatment for Venous Reflux): In the context of vein disorders of the legs, this describes therapeutic pressure designed to prevent blood from pooling in the legs. This usually comes in the form of tight-fitting compression hose or socks.
Compression Garments: It is important after undergoing vein surgery to wear compression garments to avoid swelling and bruising of the operated area.
Compression Stockings: Compression stockings for women include compression pantyhose, compression leggins and compression socks for maternity. Compression stockings also can be used for casual purposes.
Cosmetic surgery: The procedures, techniques, and principles of cosmetic surgery are completely focused on enhancing a patient’s appearance.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): A blood clot that forms in a vein deep in the body. Most deep vein clots occur in the lower leg or thigh. If the vein swells, the condition is called thrombophlebitis. A deep vein thrombosis can break loose and cause a serious problem in the lung, called a pulmonary embolism. A deep vein thrombosis can cause leg pain or swelling, but also can occur with no symptoms.
Dermal Filler: Can plump thin lips, enhance shallow contours, soften facial creases, remove wrinkles and improve the appearance of recessed scars.
Dilated Blood Vessels: The opening up or enlargement of blood vessels that is controlled by the action of certain hormones on the muscular lining of the vessels. This allows more or less blood to flow to in limbs or organs in response to variations in factors such as activity and temperature.
Doppler Ultrasound exam: A test that uses sound waves to assess the blood flow in large arteries and veins. It is a non-invasive procedure.
Edema: A general term for a collection of fluid anywhere in the body. It is similar to swelling, but more severe, and is a common symptom of patients with vein disease.
Endovenous Vein Ablation: A minimally invasive surgical approach used to collapse a diseased vein. It relies upon a heat-producing catheter inserted into the vein.
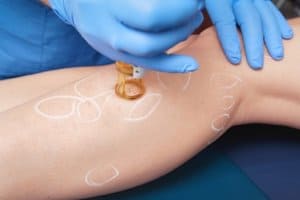
Laser Spider Vein Treatment: Treating clusters of spider veins using a skin resurfacing laser. This treatment is non-invasive and permanent.
Leg Vein: In the context of vein disease, this usually refers to the two main veins in the leg. The anterior (front) vein is the Great Saphenous Vein (GSV), and the posterior (rear) vein is the Small Saphenous Vein (SSV).
Medical Adhesive: A surgical-grade adhesive used to close down diseased or ruptured blood vessels. It is often used in the treatment of diseased leg veins.
Microphlebectomy: Surgical removal of varicose veins of the legs. This procedure is usually performed in an outpatient environment using local anesthetic.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Damage to the smaller arteries of the extremities, usually the legs. This is often a result of atherosclerosis, the process by which cholesterol deposits in arteries.
Phlebectomy: A general term used to describe surgical removal of an unwanted vein on the surface of the skin. Usually performed on varicose veins of the legs.
Phlebitis: Inflammation or irritation of a vein. When this is due to the formation of a blood clot it is known as thrombophlebitis.
Polidocanol: A dietary supplement taken to improve circulation in the legs. It is a non-synthetic chemical derived from cane sugar.
Post Phlebitis Syndrome: This condition is one of the possible complications of having a blood clot in the deep venous system (Deep Vein Thrombosis, or DVT). When this occurs in the legs, symptoms include a brownish or reddish discoloration of the skin, pain, heaviness, itching or burning, swelling, varicose veins, and ulcers.
Pulmonary Embolism: When a piece of a blood clot breaks off and enters the blood this is known as an embolism. When an embolism lodges in the lungs it becomes a pulmonary embolism, which can be life threatening.
Peripheral Venous Disease (PVD): Damage to, or disease of, the smaller veins of the extremities, usually the legs. This is often a direct result of venous reflux disease.
Is it possible to treat vein problems on your own?
While you can take some steps to manage and alleviate symptoms of vein problems at home, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Here are some self-care measures that can help with vein issues:
- Compression Stockings: Wearing compression stockings can help improve blood flow and reduce swelling and discomfort in your legs.
- Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can improve circulation and strengthen the muscles that support your veins.
- Elevate Your Legs: Elevating your legs above heart level for 15-30 minutes several times a day can help reduce swelling and improve blood flow.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Keeping a healthy weight can reduce pressure on your veins and improve overall vascular health.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Try to change your position frequently to encourage blood flow. If you must sit or stand for long periods, take breaks to move around.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep your blood thin and promotes better circulation.
When to look for a doctor?
You should seek medical advice from a doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms or conditions related to vein problems:
- Persistent Pain or Discomfort: If you have ongoing pain, aching, or discomfort in your legs, especially if it worsens after prolonged sitting or standing.
- Swelling: Noticeable swelling in your legs, ankles, or feet that doesn’t improve with elevation or compression stockings.
- Visible Varicose Veins: Large, bulging, or twisted veins that are painful or cause significant discomfort.
- Skin Changes: Changes in the skin around the affected veins, such as discoloration, thickening, or ulceration.
- Bleeding Veins: If a varicose vein starts to bleed, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly.
